Understanding Ovarian Cancer: Diagnosis, Treatment & Support
What is Ovarian Cancer?
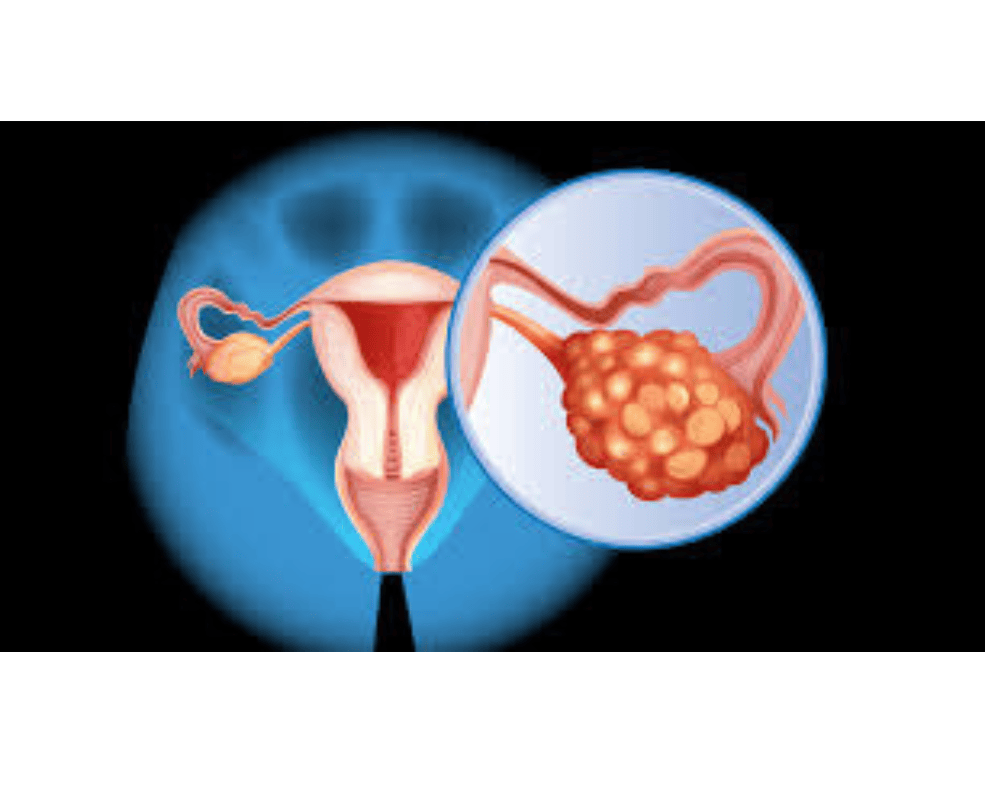
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, the reproductive glands that produce eggs in women. It is one of the most challenging cancers to detect early because symptoms are often subtle or mistaken for other conditions. There are three main types of ovarian cancer: epithelial (the most common), germ cell, and stromal tumors. Early diagnosis improves treatment outcomes, making awareness of risk factors and symptoms critical.
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, the reproductive glands that produce eggs in women. It is one of the most challenging cancers to detect early because symptoms are often subtle or mistaken for other conditions. There are three main types of ovarian cancer: epithelial (the most common), germ cell, and stromal tumors. Early diagnosis improves treatment outcomes, making awareness of risk factors and symptoms critical.
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer, including:
- Age: Most cases occur in women over 50, especially post-menopausal women.
- Family History: A family history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer increases the risk.
- Genetic Mutations: BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations are strongly linked to ovarian cancer.
- Reproductive History: Women who have never been pregnant or had their first pregnancy after 35 may have a higher risk.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it, linked to ovarian cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use of estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy after menopause can increase risk.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer, including:
- Age: Most cases occur in women over 50, especially post-menopausal women.
- Family History: A family history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer increases the risk.
- Genetic Mutations: BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations are strongly linked to ovarian cancer.
- Reproductive History: Women who have never been pregnant or had their first pregnancy after 35 may have a higher risk.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside it, linked to ovarian cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use of estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy after menopause can increase risk.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer symptoms are often vague but may include:
- Persistent bloating or abdominal swelling.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly.
- Urinary urgency or frequency.
- Fatigue, back pain, and weight loss.
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding.
Ovarian cancer symptoms are often vague but may include:
- Persistent bloating or abdominal swelling.
- Pelvic or abdominal pain.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly.
- Urinary urgency or frequency.
- Fatigue, back pain, and weight loss.
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding.
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing ovarian cancer typically involves:
- Pelvic Exam: A routine pelvic exam can detect abnormal masses or growths.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): This imaging test uses sound waves to view the ovaries and detect abnormalities.
- CA-125 Blood Test: A protein marker that can be elevated in women with ovarian cancer, though it is not always reliable for early detection.
- CT Scans and MRI: Used to determine the extent and spread of the cancer.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue is taken and analyzed to confirm the presence of cancer.
Diagnosing ovarian cancer typically involves:
- Pelvic Exam: A routine pelvic exam can detect abnormal masses or growths.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): This imaging test uses sound waves to view the ovaries and detect abnormalities.
- CA-125 Blood Test: A protein marker that can be elevated in women with ovarian cancer, though it is not always reliable for early detection.
- CT Scans and MRI: Used to determine the extent and spread of the cancer.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue is taken and analyzed to confirm the presence of cancer.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cancer
The treatment approach depends on the cancer stage and type:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for ovarian cancer. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This often involves the removal of one or both ovaries, the fallopian tubes, and sometimes the uterus.
- Chemotherapy: Often used after surgery to target any remaining cancer cells. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy (delivered directly to the abdomen) may be used in some cases.
- Radiation Therapy: Less commonly used but may be recommended for specific cases where localized treatment is needed.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs like PARP inhibitors (e.g., olaparib) target cancer cells’ ability to repair DNA, making them more susceptible to treatment.
The treatment approach depends on the cancer stage and type:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for ovarian cancer. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This often involves the removal of one or both ovaries, the fallopian tubes, and sometimes the uterus.
- Chemotherapy: Often used after surgery to target any remaining cancer cells. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy (delivered directly to the abdomen) may be used in some cases.
- Radiation Therapy: Less commonly used but may be recommended for specific cases where localized treatment is needed.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs like PARP inhibitors (e.g., olaparib) target cancer cells’ ability to repair DNA, making them more susceptible to treatment.
Newer Treatment Modalities
- HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy): This innovative treatment involves delivering heated chemotherapy directly into the abdomen after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- PARP Inhibitors: A newer class of drugs used in patients with BRCA mutations or after the failure of initial treatments. These drugs prevent cancer cells from repairing themselves.
- Hormonal Therapy: In certain cases, hormone-blocking treatments may be used to slow the growth of ovarian cancer, especially in hormone-sensitive types.
- HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy): This innovative treatment involves delivering heated chemotherapy directly into the abdomen after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- PARP Inhibitors: A newer class of drugs used in patients with BRCA mutations or after the failure of initial treatments. These drugs prevent cancer cells from repairing themselves.
- Hormonal Therapy: In certain cases, hormone-blocking treatments may be used to slow the growth of ovarian cancer, especially in hormone-sensitive types.
Role of Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, a newer frontier in cancer treatment, aims to boost the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Drugs such as checkpoint inhibitors are being explored in ovarian cancer to improve the immune response. Though not yet a standard treatment, clinical trials are showing promising results, especially in combination with other therapies.
Immunotherapy, a newer frontier in cancer treatment, aims to boost the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Drugs such as checkpoint inhibitors are being explored in ovarian cancer to improve the immune response. Though not yet a standard treatment, clinical trials are showing promising results, especially in combination with other therapies.
Prognosis
The prognosis for ovarian cancer varies based on factors such as the stage at diagnosis and the patient’s overall health. When caught early, the 5-year survival rate can be as high as 90%. However, due to the difficulty in detecting ovarian cancer early, many cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage, where survival rates decrease. Advances in treatment, including targeted therapies and personalized medicine, are improving outcomes and offering hope for longer-term survival.
The prognosis for ovarian cancer varies based on factors such as the stage at diagnosis and the patient’s overall health. When caught early, the 5-year survival rate can be as high as 90%. However, due to the difficulty in detecting ovarian cancer early, many cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage, where survival rates decrease. Advances in treatment, including targeted therapies and personalized medicine, are improving outcomes and offering hope for longer-term survival.
Why Choose ID Cancer Center for Ovarian Cancer?
At ID Cancer Center, we are committed to providing world-class care for ovarian cancer with a patient-first approach. Here’s why you can trust us with your care:
Expert Multidisciplinary Team: Our team of gynecologic oncologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, radiologists, and genetic counselors are specialized in diagnosing and treating ovarian cancer. Our collaborative approach ensures personalized and comprehensive care at every stage.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for ovarian cancer treatment. We utilize state-of-the-art diagnostic tools such as high-resolution transvaginal ultrasound, CA-125 testing, and advanced imaging techniques like CT and MRI scans to detect ovarian cancer in its earliest stages.
Cutting-edge Treatments: From minimally invasive surgery to targeted therapies like PARP inhibitors, we offer the latest, most effective treatments for ovarian cancer. Our center is equipped with innovative modalities like HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy), giving patients access to leading-edge treatments that aren’t widely available elsewhere.
Access to Clinical Trials: As a research-driven institution, ID Cancer Center offers access to cutting-edge clinical trials for ovarian cancer. This allows our patients to benefit from emerging therapies, such as new immunotherapies and combination treatments that may not be available elsewhere.
Personalized Care Plans: We tailor every treatment plan to the unique needs of each patient, based on factors like genetics, cancer type, and overall health. Our genetic counseling services can help identify risks linked to BRCA mutations and guide personalized treatment strategies.
Supportive Care Throughout: At ID Cancer Center, we believe in holistic, compassionate care. We offer comprehensive support services including nutritional counseling, psychological support, and survivorship care to ensure that patients are not only physically treated but also emotionally supported throughout their journey.
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up: Our commitment to your well-being extends beyond treatment. With regular follow-up care, we monitor your progress, help manage any side effects, and offer guidance on maintaining your health after treatment.
At ID Cancer Center, you’re not just a patient – you’re part of a community dedicated to helping you navigate ovarian cancer with confidence and care. We provide the expertise, innovation, and compassion needed to give you the best possible outcome.
At ID Cancer Center, we are committed to providing world-class care for ovarian cancer with a patient-first approach. Here’s why you can trust us with your care:
Expert Multidisciplinary Team: Our team of gynecologic oncologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, radiologists, and genetic counselors are specialized in diagnosing and treating ovarian cancer. Our collaborative approach ensures personalized and comprehensive care at every stage.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for ovarian cancer treatment. We utilize state-of-the-art diagnostic tools such as high-resolution transvaginal ultrasound, CA-125 testing, and advanced imaging techniques like CT and MRI scans to detect ovarian cancer in its earliest stages.
Cutting-edge Treatments: From minimally invasive surgery to targeted therapies like PARP inhibitors, we offer the latest, most effective treatments for ovarian cancer. Our center is equipped with innovative modalities like HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy), giving patients access to leading-edge treatments that aren’t widely available elsewhere.
Access to Clinical Trials: As a research-driven institution, ID Cancer Center offers access to cutting-edge clinical trials for ovarian cancer. This allows our patients to benefit from emerging therapies, such as new immunotherapies and combination treatments that may not be available elsewhere.
Personalized Care Plans: We tailor every treatment plan to the unique needs of each patient, based on factors like genetics, cancer type, and overall health. Our genetic counseling services can help identify risks linked to BRCA mutations and guide personalized treatment strategies.
Supportive Care Throughout: At ID Cancer Center, we believe in holistic, compassionate care. We offer comprehensive support services including nutritional counseling, psychological support, and survivorship care to ensure that patients are not only physically treated but also emotionally supported throughout their journey.
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up: Our commitment to your well-being extends beyond treatment. With regular follow-up care, we monitor your progress, help manage any side effects, and offer guidance on maintaining your health after treatment.
At ID Cancer Center, you’re not just a patient – you’re part of a community dedicated to helping you navigate ovarian cancer with confidence and care. We provide the expertise, innovation, and compassion needed to give you the best possible outcome.
